Dual-band WiFi offers faster speeds and less interference than single-band WiFi. It uses two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band has a better range but slower speeds, while the 5 GHz band has faster speeds but a shorter range.
Overview of Dual Band Vs. Single Band WiFi
| Aspect | Dual Band WiFi | Single Band WiFi |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Bands | Operates on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands | Operates on the 2.4GHz band only |
| Speed | Faster speeds due to the 5GHz band | Slower speeds, limited to 2.4GHz |
| Interference | Reduced interference and congestion | More susceptible to interference |
| Range | Slightly shorter range on 5GHz band | Longer range due to the 2.4GHz band |
| Device Compatibility | Compatible with modern devices | Compatible with older devices |
| Signal Penetration | Better for walls and obstacles | Weaker penetration through obstacles |
| Crowded Environments | Ideal for crowded areas with multiple devices | Prone to congestion and slowdown |
| Streaming and Gaming | Excellent for high-bandwidth activities | Limited for bandwidth-intensive tasks |
| Compatibility | Compatible with both 2.4GHz and 5GHz devices | Compatible with 2.4GHz devices |
| Dual Band Router Usage | Routers have both 2.4GHz and 5GHz radios | Routers have only 2.4GHz radio |
| Overall Performance | Offers improved performance and reliability | Basic performance for simple tasks |
Basics of Single-Band WiFi
Single-band Wi-Fi refers to a wireless network that operates solely on the 2.4 GHz frequency band. It is one of the older and more widely used Wi-Fi standards. Here are the basics of single-band Wi-Fi:
- Frequency Band: Single-band Wi-Fi operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This band offers good range but is more susceptible to interference from other devices operating in the same frequency range.
- Speed and Throughput: Single-band Wi-Fi has a lower maximum data transfer rate compared to dual-band Wi-Fi. Typically, single-band Wi-Fi supports data rates up to 150 Mbps or 300 Mbps, depending on the Wi-Fi standard being used (e.g., 802.11n).
- Range: Wi-Fi signals in the 2.4 GHz band have better range and can penetrate obstacles like walls and furniture more effectively than higher frequency bands. This makes single-band Wi-Fi suitable for larger coverage areas.
- Interference: The 2.4 GHz band is crowded, as many other devices like Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, and microwaves also use this frequency. This can result in more interference, potentially impacting the Wi-Fi signal quality and performance.
- Device Compatibility: Single-band Wi-Fi is compatible with a wide range of devices, including older devices that may not support dual-band Wi-Fi. Most smartphones, laptops, tablets, and IoT devices are compatible with single-band Wi-Fi networks.
- Channel Availability: The 2.4 GHz band offers a limited number of channels, typically 11 or 13, depending on the region. However, there are only three non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11), which can be used to minimize interference from neighboring networks.
- Suitable Use Cases: Single-band Wi-Fi is suitable for basic internet browsing, email, and light streaming tasks. It is often used in residential settings or small offices where there are minimal interference sources and the network demands are not high.
Advantages of Single-Band WiFi
Single-band Wi-Fi, operating on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, offers several advantages in specific situations:
- Compatibility: Single-band Wi-Fi is compatible with a wide range of devices, including older devices that may not support dual-band Wi-Fi. This ensures that various devices can connect to the network without compatibility issues.
- Better Range: Wi-Fi signals in the 2.4 GHz band have a better range compared to higher frequency bands. They can penetrate obstacles like walls and furniture more effectively, making single-band Wi-Fi suitable for larger coverage areas.
- Lower Interference: The 2.4 GHz band, although crowded, generally experiences less interference than the 5 GHz band. This is because many other devices like Bluetooth devices and microwaves primarily operate in the 2.4 GHz range, leaving the 5 GHz band less congested.
- Longer Battery Life: Devices connected to a single-band Wi-Fi network may experience longer battery life compared to those connected to a dual-band network. This is because operating in the 2.4 GHz band typically requires less power consumption.
- Cost-Effective: Single-band Wi-Fi routers and devices tend to be more affordable compared to their dual-band counterparts. This makes single-band Wi-Fi an economical choice, especially for basic internet browsing and light streaming needs.
- Simplified Network Setup: With only one frequency band to manage, setting up and configuring a single-band Wi-Fi network is often simpler and less complex than a dual-band network. This can be advantageous for users who prefer a straightforward setup process.
- Wider Signal Coverage: Due to the lower frequency of the 2.4 GHz band, single-band Wi-Fi signals can cover a wider area compared to higher frequency bands. This makes it well-suited for environments where signal coverage is a priority.
Limitations and Drawbacks of Single-Band WiFi
While single-band Wi-Fi has its advantages, it also comes with several limitations and drawbacks:
- Limited Speed: Single-band Wi-Fi typically offers lower maximum data transfer rates compared to dual-band Wi-Fi. This limitation can impact the performance of bandwidth-intensive activities such as HD streaming or online gaming.
- Interference Susceptibility: The 2.4 GHz frequency band used by single-band Wi-Fi is crowded, as it is shared with other devices like Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, and microwaves. This high level of interference can result in degraded signal quality and slower speeds.
- Congestion: Since the 2.4 GHz band has a limited number of available channels, multiple Wi-Fi networks operating nearby can cause interference and network congestion. This can lead to reduced performance and slower data speeds, especially in densely populated areas.
- Channel Overlapping: In the 2.4 GHz band, only three non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11) are available, which limits the options for minimizing interference from neighboring networks. This channel overlapping can further impact the signal quality and overall network performance.
- Limited Device Support: Single-band Wi-Fi may not support newer devices that are capable of connecting to dual-band networks. Devices that are only compatible with the 5 GHz band may not be able to connect to single-band Wi-Fi networks.
- Potential Signal Interference: Interference from other electronic devices operating in the 2.4 GHz band, such as microwaves or certain wireless gadgets, can disrupt the Wi-Fi signal and lead to connection issues.
- Bandwidth Sharing: In single-band Wi-Fi networks, all connected devices share the available bandwidth. As more devices connect simultaneously, the bandwidth is divided, potentially resulting in slower speeds for each device.
- Future Compatibility: As technology advances, newer devices and standards may rely more on the higher frequency bands of dual-band Wi-Fi. Single-band Wi-Fi networks may become less compatible with future devices, limiting their long-term usability.
Basics of Dual Band WiFi
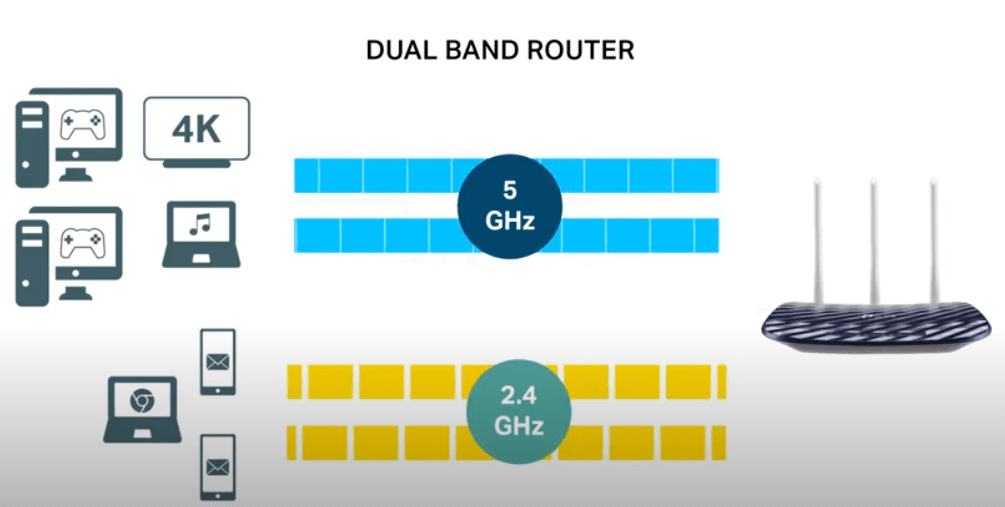
Dual-band Wi-Fi is a wireless network technology that operates on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Here are the basics of dual-band Wi-Fi:
- Frequency Bands: Dual-band Wi-Fi utilizes both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. The 2.4 GHz band provides better range, while the 5 GHz band offers higher data rates and reduced interference.
- 2.4 GHz Band: The 2.4 GHz band is commonly used and has a longer range. It is suitable for devices that are farther away from the router or for areas with obstacles that can obstruct the Wi-Fi signal.
- 5 GHz Band: The 5 GHz band provides faster speeds but has a shorter range compared to the 2.4 GHz band. It is ideal for devices located closer to the router and for environments with a higher density of devices.
- Simultaneous Dual Band: Some dual-band Wi-Fi routers support simultaneous dual band, allowing devices to connect to either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band based on their capabilities and requirements. This provides flexibility and ensures optimal performance for various devices.
- Channel Selection: Dual-band Wi-Fi offers more available channels compared to single-band Wi-Fi, reducing interference from neighboring networks. The 2.4 GHz band has up to 11 channels, while the 5 GHz band has significantly more, typically around 24.
- Interference Mitigation: The 5 GHz band is less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band, as it is used by fewer devices. This reduces the likelihood of interference and improves overall network performance.
- Device Compatibility: Dual-band Wi-Fi supports a wide range of devices, including older devices that only operate on the 2.4 GHz band. Newer devices with dual-band capabilities can take advantage of the higher speeds and reduced congestion on the 5 GHz band.
- Band Steering: Dual-band Wi-Fi routers may feature band steering, which automatically directs compatible devices to the optimal frequency band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz) based on their capabilities and signal strength. This ensures devices are connected to the most suitable band for optimal performance.
- Application-Based Band Selection: Some routers offer the option to assign specific devices or applications to a particular frequency band. This allows for more precise control over bandwidth allocation and can optimize performance for specific tasks or devices.
Advantages of Dual Band WiFi
Dual-band Wi-Fi offers several advantages over single-band Wi-Fi, making it a preferred choice for many users:
- Faster Speeds: The 5 GHz band used in dual-band Wi-Fi offers higher data rates compared to the 2.4 GHz band. This translates into faster internet speeds and improved performance for bandwidth-intensive activities like HD streaming, online gaming, and large file downloads.
- Reduced Interference: The 5 GHz band is less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band, as it is used by fewer devices. This reduces the likelihood of interference from neighboring Wi-Fi networks and other devices, resulting in a more stable and reliable connection.
- Enhanced Network Capacity: Dual-band Wi-Fi provides the ability to distribute devices across two frequency bands, reducing congestion and allowing for better utilization of available network resources. This is particularly beneficial in environments with multiple devices, such as busy homes or offices.
- Flexibility and Compatibility: Dual-band Wi-Fi routers support both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of devices. Older devices that only support 2.4 GHz can connect, while newer devices that support both bands can take advantage of the faster speeds and reduced interference on the 5 GHz band.
- Improved Range and Coverage: While the 2.4 GHz band offers better range, the 5 GHz band provides faster speeds over shorter distances. By utilizing both bands, dual-band Wi-Fi ensures optimal coverage throughout the home or office, allowing devices to connect to the most suitable band based on their location.
- Bandwidth Allocation: Dual-band routers often include features like band steering or application-based band selection, allowing for more precise control over bandwidth allocation. This enables prioritization of specific devices or applications to ensure they receive the necessary bandwidth for optimal performance.
- Better Streaming Experience: With dual-band Wi-Fi, streaming media content becomes smoother and more reliable. The higher speeds and reduced interference of the 5 GHz band result in improved video quality, reduced buffering, and minimized interruptions during streaming sessions.
- Future-Proofing: Dual-band Wi-Fi is compatible with newer Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), which offer advanced features and improved performance. By investing in a dual-band router, users can future-proof their network and ensure compatibility with upcoming devices and technologies.
Limitations and Considerations for Dual Band WiFi
While dual-band Wi-Fi offers numerous advantages, it is important to consider its limitations and certain factors when implementing it:
- Device Compatibility: While dual-band Wi-Fi routers support both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, not all devices are compatible with the 5 GHz band. Older devices or certain IoT devices may only support the 2.4 GHz band. Before opting for dual-band Wi-Fi, ensure that all devices you intend to connect are compatible with the 5 GHz band.
- Range Limitations: The 5 GHz band used in dual-band Wi-Fi has a shorter range compared to the 2.4 GHz band. Walls, floors, and other obstacles can further reduce the range of the 5 GHz signal. If you have devices located far from the router or in areas with significant obstructions, they may experience weaker signal strength and slower speeds when connected to the 5 GHz band.
- Interference in the 2.4 GHz Band: While the 5 GHz band offers reduced interference, the 2.4 GHz band can still be crowded due to the presence of other devices like Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, and microwaves. This can impact the performance of devices connected to the 2.4 GHz band, particularly in areas with a high density of wireless devices.
- Channel Overlapping: In the 2.4 GHz band, there are only three non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11). When neighboring networks are using the same or overlapping channels, it can result in interference and reduced performance. Selecting the optimal channel for the 2.4 GHz band is crucial to minimize interference from nearby Wi-Fi networks.
- Router Placement: To maximize the benefits of dual-band Wi-Fi, proper router placement is important. Placing the router centrally in your home or office, away from obstructions and interference sources, can help ensure better coverage and performance for both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Band Steering and Bandwidth Allocation: While band steering and application-based band selection are advantageous features of dual-band Wi-Fi routers, they require proper configuration and management. It is essential to understand how these features work and adjust the settings according to your specific network requirements.
- Cost: Dual-band Wi-Fi routers generally come at a higher price point compared to single-band routers. Consider your budget and network needs when deciding whether the additional features and benefits of dual-band Wi-Fi justify the higher cost.
- Network Complexity: Dual-band Wi-Fi networks can introduce added complexity compared to single-band networks. Managing two frequency bands, configuring band settings, and troubleshooting potential issues may require additional knowledge and effort.
Key Differences between Dual Band and Single Band WiFi
Dual-band and single-band Wi-Fi have distinct differences that impact their performance and capabilities:
- Frequency Bands: The main difference between dual-band and single-band Wi-Fi is the number of frequency bands they operate on. Single-band Wi-Fi operates on the 2.4 GHz band, while dual-band Wi-Fi operates on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Speed and Performance: Dual-band Wi-Fi offers faster speeds and better performance compared to single-band Wi-Fi. The 5 GHz band used in dual-band Wi-Fi provides higher data transfer rates, making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks like HD streaming and online gaming.
- Interference and Congestion: The 2.4 GHz band used in single-band Wi-Fi is more crowded and prone to interference from other devices operating in the same frequency range, such as Bluetooth devices and microwaves. Dual-band Wi-Fi mitigates this issue by offering the less congested 5 GHz band, resulting in reduced interference and improved network performance.
- Range and Coverage: Single-band Wi-Fi typically has better range compared to the 5 GHz band of dual-band Wi-Fi. The lower frequency of the 2.4 GHz band allows the signal to penetrate obstacles and travel longer distances. However, the 5 GHz band of dual-band Wi-Fi provides faster speeds over shorter distances.
- Device Compatibility: Single-band Wi-Fi is compatible with a wide range of devices, including older devices that only support the 2.4 GHz band. On the other hand, dual-band Wi-Fi offers compatibility with both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz capable devices, allowing for optimal performance and improved network management.
- Network Capacity: Dual-band Wi-Fi offers increased network capacity compared to single-band Wi-Fi. With two frequency bands available, dual-band routers can distribute devices across both bands, reducing congestion and improving overall network performance, especially in environments with multiple connected devices.
- Price: Dual-band Wi-Fi routers typically come at a higher price point compared to single-band routers due to their additional capabilities and features. The added performance and flexibility of dual-band Wi-Fi justify the higher cost for users who require faster speeds and better network management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different aspects of Wi-Fi technology is essential for optimizing network connectivity. From accessing routers without the internet to exploring Firestick options and limitations, and from the basics of single-band and dual-band Wi-Fi to troubleshooting common issues, each topic plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless wireless experience.
References:
https://www.rango.net/blog/dual-band-vs-single-band-router
https://www.gadgetreview.com/router-single-band-vs-dual-band
Hello, I’m Herman C. Miller, the founder of InternetPKG.com, your ultimate destination for all things Mobile Internet and Telecommunication Services. With a BSc in Telecommunication Services and over 6 years at AT&T, my passion for the industry led to this platform. At InternetPKG.com, we prioritize keeping you informed with the latest package offers, ensuring our content stays current. Our team, including a dedicated Internet Package and Mobile Data Plans Researcher, tirelessly researches emerging trends, identifies market opportunities, and provides expert product recommendations.
